NextJs: Why It's the Ultimate Framework for Building Powerful Web Applications
April 26th, 2023 — 10 min read

April 26th, 2023 — 10 min read

Next.js is a popular React framework that enables developers to build powerful web applications with ease. It provides a wide range of features that make building web applications faster and more efficient:
In this blog post, we’ll take a closer look at what Next.js can do.
Server-side rendering (SSR) is the process of generating HTML on the server-side instead of the client-side. This means that when a user requests a web page, the server generates the HTML, and then sends it to the client, which is then displayed in the user's browser. While client-side rendering (CSR) has become increasingly popular with the advent of JavaScript frameworks like React, there are still several benefits to using SSR that make it a valuable tool in web development.
Improved page load times
One of the primary benefits of SSR is faster page load times. Since the HTML is generated on the server and sent to the client as a complete document, the user's browser can start rendering the page immediately. With Client Side Rendering, the browser has to wait for the JavaScript to download and execute before it can start rendering the page, which can lead to longer load times, especially on slower connections. Also, it can improve caching so the bandwindth usage on the server is lower.
Better search engine optimization (SEO)
Another benefit of SSR is improved SEO. Search engine crawlers can easily read and index the HTML generated on the server, whereas with Client Side Rendering, crawlers may have difficulty parsing the JavaScript code to understand the content of the page. This means that pages rendered with SSR are more likely to appear higher in search engine results pages (SERPs) and get more organic traffic.
Accessibility and usability improvements
SSR can also improve accessibility and usability for users who may have slower internet connections or older browsers. Because the HTML is generated on the server, it is more likely to be compatible with a wider range of devices and browsers, and can be delivered more reliably to users with slower connections.
Improved security
With SSR, it's possible to control what data is sent to the client, which can help prevent attacks like cross-site scripting (XSS) and other security vulnerabilities. Since the server generates the HTML, it can sanitize user input and remove potentially dangerous code before it is sent to the client.
Better performance on mobile devices
Finally, SSR can improve performance on mobile devices. Mobile users often have slower connections and less powerful hardware than desktop users, which can make client-side rendering slower and more resource-intensive. With SSR, the server does most of the heavy lifting, which means that mobile users can get a faster and smoother browsing experience.
Next.js also supports static site generation (SSG). With SSG, the server generates the HTML pages at build time rather than runtime. This can help improve the performance of web applications by reducing the time it takes to load each page. Additionally, SSG can also help improve the SEO of your website by making it easier for search engines to crawl your pages.
Image optimization is the process of reducing the file size of images without sacrificing their quality. It involves compressing and resizing images to make them smaller and faster to load, which can help improve website performance and reduce bandwidth usage.
How does Next.js handle image optimization?
Next.js provides built-in image optimization using the Image component. This component allows you to render images with different sizes and formats based on the device and screen size of the user, ensuring that only the necessary image data is loaded. This helps reduce the amount of data that needs to be downloaded, improving website performance and reducing load times.
How effective is the image optimization?
The image optimization provided by Next.js is highly effective in reducing the file size of images and improving website performance. The Image component automatically generates and serves different sizes and formats of images based on the user's device and screen size, which helps reduce the amount of data that needs to be downloaded and improves load times.
To demonstrate how image optimization can improve website performance, let's consider an example of an image on our webpage. We will conduct an experiment by comparing the loading time of the image on two different types of internet connections: a fast one and a slow one.

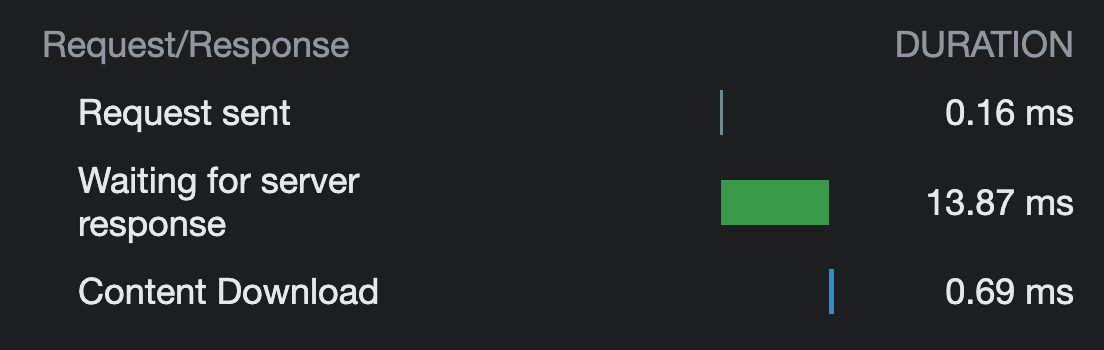
Upon inspection, we can observe that the unoptimized version of the content took 1.71 miliseconds to download, while the optimized version only took 0.69 miliseconds. This translates to a 60% improvement in download speed for the optimized version when compared to the unoptimized version, disregarding the server response time.
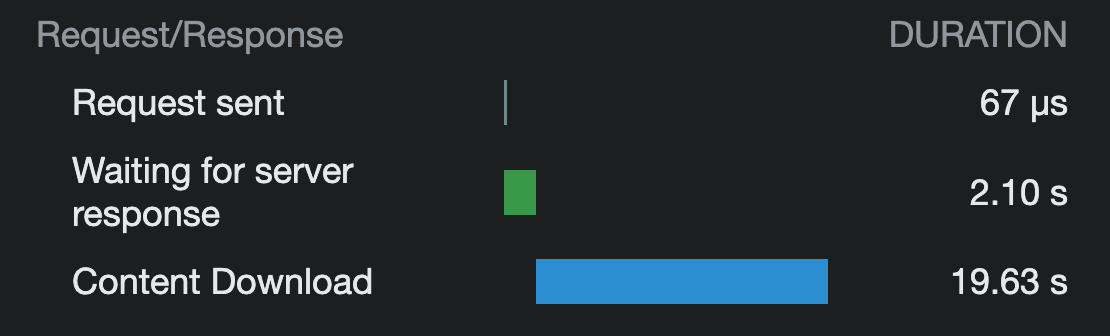
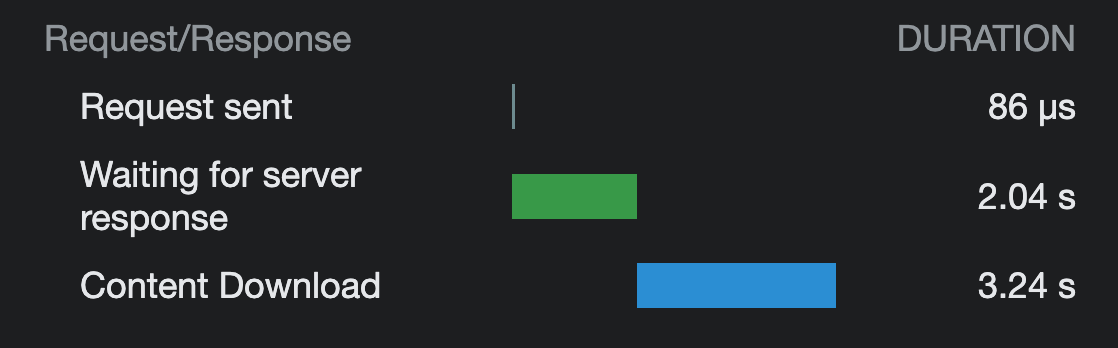
When dealing with a slow internet connection, the benefits of image optimization become even more apparent. In our observation, the unoptimized version of the content took 19.63 seconds to download, while the optimized version took only 3.24 seconds. This corresponds to a remarkable 84% improvement in download speed for the optimized version compared to the unoptimized version, regardless of server response time.
These results highlight the importance of optimizing your web application for all users, especially those with slower internet connections. In such cases, image optimization becomes even more crucial in order to improve website performance, reduce load times, and enhance the user experience.
Lazy loading is a technique used to improve the performance of web applications by deferring the loading of non-critical resources until they are actually needed. In the context of Next.js, lazy loading is used to optimize the loading of images, videos, and other media content.
Next.js provides built-in support for lazy loading through the use of the "lazy" attribute. This attribute allows you to specify which resources should be loaded lazily and when they should be loaded. In this article, we'll take a closer look at how lazy loading works in Next.js and how it can be used to improve website performance.
How Lazy Loading Works in Next.js
In Next.js, lazy loading works by splitting the code into smaller chunks, called "chunks." These chunks contain the code that is needed to render a particular component or page. When a user requests a page, only the chunks that are necessary for that page are loaded. This means that the initial page load is faster, as only the essential resources are loaded.
When lazy loading images or other media content, the "lazy" attribute can be added to the HTML tag. This attribute tells the browser to defer the loading of the resource until it is actually needed. For example, if an image is below the fold (i.e., not visible on the screen), the browser will not load the image until the user scrolls down to it.
Benefits of Lazy Loading in Next.js
There are several benefits to using lazy loading in Next.js. First, lazy loading can significantly improve the performance of your website by deferring the loading of non-critical resources. This means that the initial page load is faster, which can help improve user experience and reduce bounce rates.
Second, lazy loading can reduce the amount of data that needs to be downloaded, which can help reduce bandwidth usage and improve website speed. This is particularly important for users on slower internet connections or mobile devices.
Finally, lazy loading can help improve website accessibility by reducing the amount of content that needs to be loaded before the user can interact with the website. This can be particularly beneficial for users with disabilities or those using assistive technologies.
API routes in Next.js provide a simple and efficient way to create server-side API endpoints for your web application. With Next.js API routes, you can create custom endpoints to handle HTTP requests and responses, allowing you to easily integrate your application with external services or APIs.
In this article, we'll explore the basics of API routes in Next.js and how you can use them to build powerful and flexible APIs.
What are API Routes in Next.js?
API routes are a way to define server-side endpoints for your Next.js application. They allow you to handle HTTP requests and responses without the need for a separate server or middleware.
Handling Different HTTP Methods
Next.js API routes allow you to define separate functions for handling different HTTP methods. For example, you could define separate functions for handling GET and POST requests to the same endpoint.
Next.js API routes provide a simple and efficient way to create server-side API endpoints for your web application. With API routes, you can easily handle HTTP requests and responses without the need for a separate server or middleware.
By defining separate API routes for different endpoints and HTTP methods, you can create powerful and flexible APIs that can integrate with external services or APIs.
Whether you're building a simple web application or a complex API-driven platform, Next.js API routes are a powerful tool that can help you build robust and scalable server-side APIs.
Proxy
In computer networking, a proxy is an intermediary server that sits between a client and a server, forwarding client requests to the server and returning responses to the client. Proxies are commonly used to provide access control and security, as well as to improve performance by caching frequently requested resources.
In the context of Next.js, proxying refers to the process of forwarding HTTP requests from a Next.js application to another server or API. This can be useful if your application needs to access external resources, such as a third-party API or a database, that are not accessible from the client-side.
By using Next.js's built-in support for proxying, you can easily create powerful and flexible APIs that can integrate with external resources and services. Whether you're building a simple web application or a complex API-driven platform, Next.js's proxying capabilities can help you build robust and scalable server-side APIs.
Stay tuned for an upcoming article that will delve into the intricacies of using a proxy in Next.js. We'll explore the many advantages, use cases, and benefits of this powerful feature.